[the_ad id=”6076″]
Acne is a common skin condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Among its various forms, hormonal acne stands out as a distinct subtype, primarily affecting individuals during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Understanding the causes, signs and symptoms, available treatments, home remedies, and precautions can empower individuals to effectively manage and prevent hormonal acne. In this blog post, we will explore hormonal acne in detail, using medical information, facts, and figures.
Causes of Hormonal Acne
Hormonal acne is primarily caused by fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly androgens such as testosterone. These hormones stimulate the production of sebum, an oily substance that helps keep the skin lubricated. However, excess sebum production can lead to clogged pores, creating an ideal environment for acne-causing bacteria to thrive. Hormonal changes during puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause can trigger these fluctuations, making individuals more prone to hormonal acne.
Hormonal acne can affect both men and women alike. In women, it is more common post 30 years of age.
Signs and Symptoms
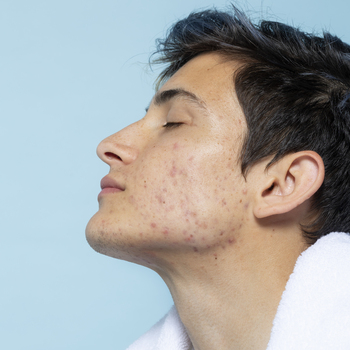
Hormonal acne often manifests as deep, painful cysts or nodules that develop mainly on the lower face, jawline, and chin. These lesions are typically larger and more inflamed than regular acne pimples. Other common signs and symptoms of hormonal acne include blackheads, whiteheads, pustules, and redness. It is important to note that everyone’s experience with hormonal acne can vary, and some individuals may have milder or more severe symptoms.
Treatment Options
Treating hormonal acne requires a comprehensive approach that targets both the underlying hormonal imbalances and the acne itself. Here are some effective treatment options:
- Topical Medications: Prescription creams or gels containing ingredients like retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, or salicylic acid can help reduce inflammation and unclog pores. These medications may need to be applied regularly for several weeks or months to see noticeable improvements.
- Oral Medications: In some cases, dermatologists may prescribe oral medications to regulate hormone levels and manage hormonal acne. Oral contraceptives, anti-androgens, and certain antibiotics can be used to control hormonal fluctuations and reduce acne symptoms.
- Isotretinoin (branded as Accutane in the US): This powerful oral medication is reserved for severe cases of acne, including hormonal acne that has not responded to other treatments. It works by reducing oil production and shrinking oil glands, leading to a significant improvement in acne symptoms. However, it requires close monitoring due to potential side effects. It is a prescription medicine.
- Light Therapy: Photodynamic therapy and laser treatments have shown promising results in managing acne. These treatments work by killing acne-causing bacteria, reducing inflammation, and controlling sebum production. One may need multiple sessions to achieve optimal results.
Home Remedies and Precautions
While professional medical advice should be sought for severe or persistent acne, there are some home remedies and precautions that can be incorporated into a skincare routine to help manage hormonal acne:
- Gentle Cleansing: Cleanse the face twice a day using a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove excess oil, dirt, and bacteria without stripping the skin’s natural moisture/healthy microbes. Prefer mild alcohol based face cleaners over soap-based ones. Washing off all the oil from the face far too often can trigger more sebum production.
- Regular Exfoliation: Use a gentle exfoliant once or twice a week to remove dead skin cells and unclog pores. Avoid aggressive scrubbing, as it can worsen inflammation. Red chickpea flour, chickpea flour, orange peel, millet flour face packs help with exfoliation.
- Non-comedogenic Products: Choose skincare and cosmetic products labelled as non-comedogenic, which are less likely to clog pores and contribute to acne breakouts.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate hormonal imbalances, leading to increased acne flare-ups. Work on reducing stress by engaging in exercise, meditation, and adequate sleep.
- Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall skin health. Avoid foods high in refined sugars and processed oils, which can contribute to inflammation.
Conclusion
Hormonal acne can be a distressing condition, but understanding its causes, recognizing its signs and symptoms, and knowing the available treatment options can significantly help individuals in managing and preventing breakouts. Seeking professional medical advice, following a consistent skincare routine, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can make a substantial difference in managing hormonal acne effectively. Remember, patience and consistency are key when it comes to achieving clear, healthy skin.